Introduction
Acetate, a versatile and widely-used material, finds its applications across various industries, ranging from fashion to pharmaceuticals. Its unique properties make it a preferred choice for manufacturing a diverse array of products, from clothing to packaging materials. In this article, we delve into the composition, uses, and benefits of it, shedding light on its remarkable versatility and practicality.
Understanding Acetate Composition
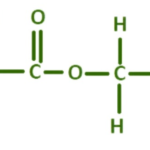
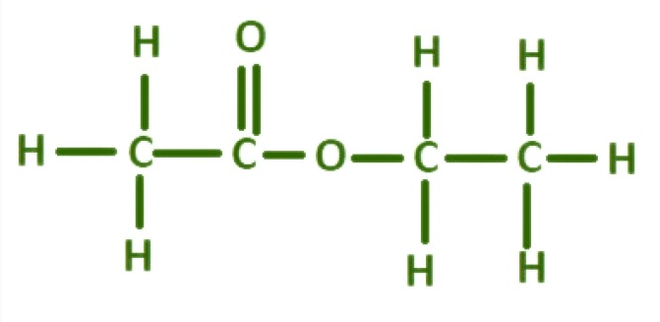
Acetate, chemically known as cellulose it, originates from natural cellulose fibers, usually sourced from wood pulp or cotton fibers. Through a series of chemical processes, cellulose undergoes treatment with acetic acid to yield cellulose it, a thermoplastic polymer renowned for its exceptional strength, durability, and flexibility. The resulting material lends itself to molding, extrusion, or spinning into various forms tailored to specific applications.
Applications of Acetate
- Fashion and Textiles: The fashion industry prizes it fabric for its luxurious feel, draping qualities, and lustrous appearance. It finds common use in the production of clothing items such as dresses, blouses, and linings, providing a lightweight and breathable alternative to natural fibers like silk.
- Eyewear: Acetate is a popular material for crafting eyeglass frames due to its lightweight nature, durability, and ability to retain vibrant colors and patterns. Eyewear made from it is valued for its aesthetic appeal, comfort, and hypoallergenic properties.
- Packaging: The packaging industry widely uses it film and sheets for their clarity, strength, and moisture resistance. They commonly serve in the production of transparent packaging materials for food products, cosmetics, and consumer goods.
- Photography: Acetate film, also known as cellulose it film, has a long history in the field of photography. It was once the primary medium for capturing and developing images before the advent of digital technology. It film is prized for its high resolution, archival stability, and ability to capture intricate details.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical: The medical and pharmaceutical industries utilize it for various purposes, including manufacturing drug delivery systems, surgical instruments, and medical implants. Its biocompatibility and versatility make it a valuable material for medical applications.
Also read this" Mary Joan Martelly: A Trailblazer in Education and Advocacy "
Conclusion
Acetate stands as a testament to the ingenuity of human innovation, offering a sustainable and versatile solution across a myriad of industries. Its unique combination of properties, including strength, flexibility, and biodegradability, makes it a prized material for applications ranging from fashion to healthcare. As we continue to explore new avenues for sustainable development, it remains a shining example of how nature-inspired materials can revolutionize our approach to design, manufacturing, and consumption.
FAQs
- Is acetate biodegradable?
Yes, acetate is biodegradable, as it is derived from natural cellulose fibers. However, the rate of biodegradation may vary depending on environmental conditions and the specific formulation of the material. - Is it possible to recycle acetate?
Yes, various processes, including chemical recycling and mechanical recycling, can recycle acetate. Recyclers can use recycled it to produce new materials, reducing the need for virgin resources and minimizing environmental impact. - Is acetate safe for use in food packaging?
Yes, regulatory agencies generally approve acetate for use in food packaging applications due to its inertness, non-toxicity, and ability to maintain product freshness and integrity. - What are the advantages of acetate over other plastics?
Acetate offers several advantages over other plastics, including biodegradability, flexibility, clarity, and resistance to chemicals and moisture. It is also renewable since it originates from natural cellulose sources. - Do any environmental concerns arise from acetate production?
While manufacturers derive acetate from natural cellulose fibers, they may subject the production process to chemical treatments and energy-intensive processes. Efforts are underway to minimize environmental impact through sustainable sourcing practices and eco-friendly production methods.